Function in C: In C language, a Function is a group or block of statements that repeat together to perform tasks. Generally, if we have to repeat the same kind of tasks multiple times then we use the function instant of writing those codes again & again.
In this post we will know in detail about Functions in C, what are the types of functions and how can we use a function in C language along with an example. So, let’s read the post which helps you to understand functions in C language.
In other words, we can say that function is the collection of statements enclosed by {}.
Benefits of function in C
We can save time by avoiding writing the same codes multiple times.
We can call a function multiple times according to our needs.
The reusability of code is the main benefit of creating a function.
The C standard library provides various built-in functions that we can call in our program. For example, we can use the strlwr() function from the string library which returns the length of a string.
We can analyze & understand a large program easily when a program is divided into multiple functions.
Define a function in C

Key terms of a function
There are three important terms in a C function
Function declaration: A function must be declared globally in a c program to tell the compiler about the function name, function parameters, and return type.
Function call: The function can be called from anywhere in the program. The parameter list must not differ in function calling and function declaration. We must pass the same number of functions as it is declared in the function declaration.
Function definition: It contains the actual statements which are to be executed. It is the most important aspect to which the control comes when the function is called. Here, we must notice that only one value can be returned from the function.
Return type: A function may return a value. The return type is the data type of the value the function returns. Some functions perform the desired operations without returning a value. In this case, the return type is the keyword void.
Parameters: When a function is invoked, you pass a value to the parameter. This value is referred to as an actual parameter or argument. The parameter list refers to the type, order, and number of the parameters of a function. Parameters are optional; that is, a function may contain no parameters.
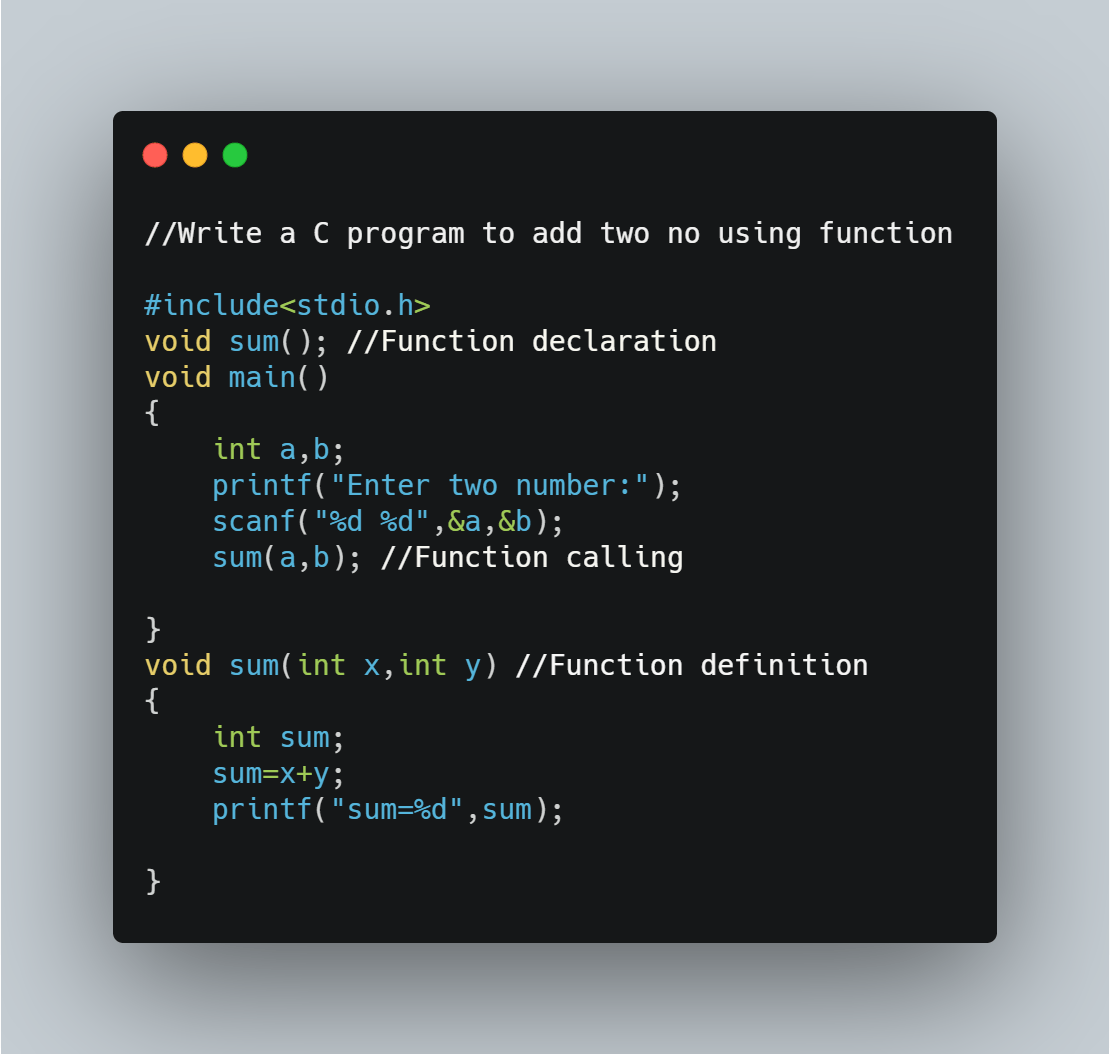
Example of using a function in C language
Types of Functions
There are two types of functions in C programming
Library Functions: Library Functions are the functions that are declared in the C header files such as scanf(), printf(), gets(), puts() etc.
User-defined functions: User-defined functions are the functions that are created by the C programmer so that he/she can use them many times. It reduces the complexity of a big program and optimizes the code.
Different aspects of function calling
A function may or may not accept any argument. It may or may not return any value. Based on these facts, there are four different aspects of function calls.
Function without arguments and without return value
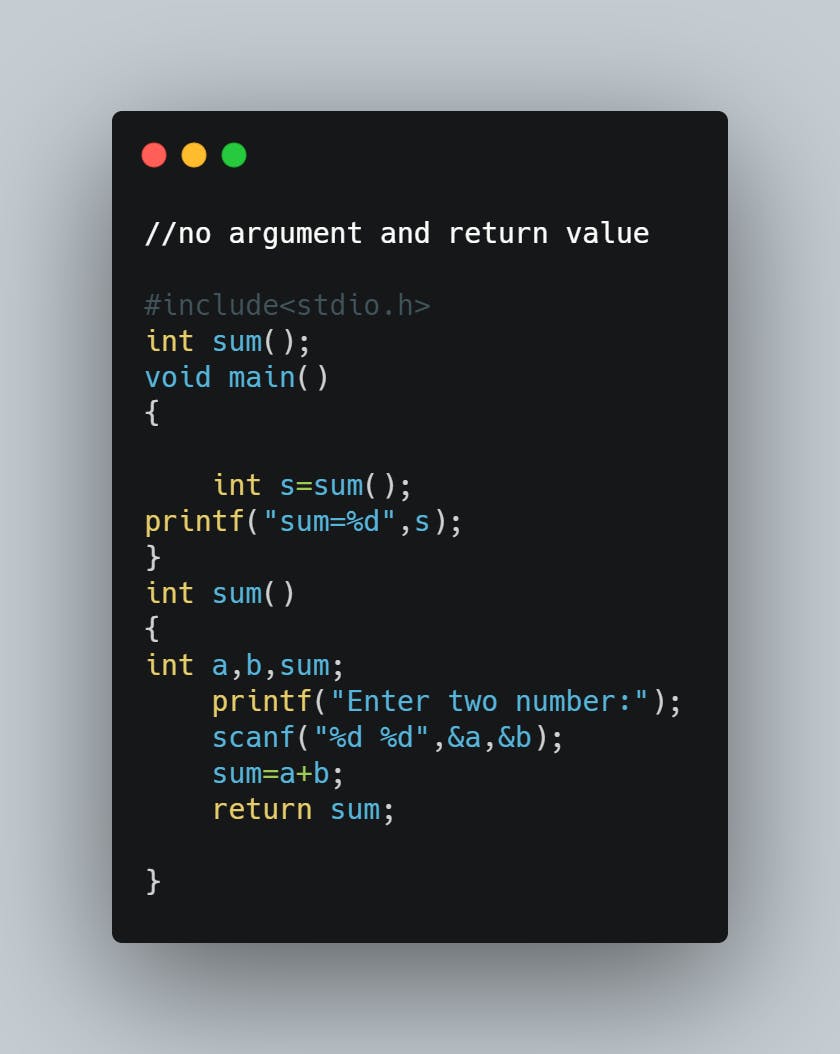
Function without arguments and with return value
Function with arguments and without return value
Function with arguments and with return value
Function without arguments and without return value: We can use the function without passing any arguments and the function will not return any value in this aspect of function calls.

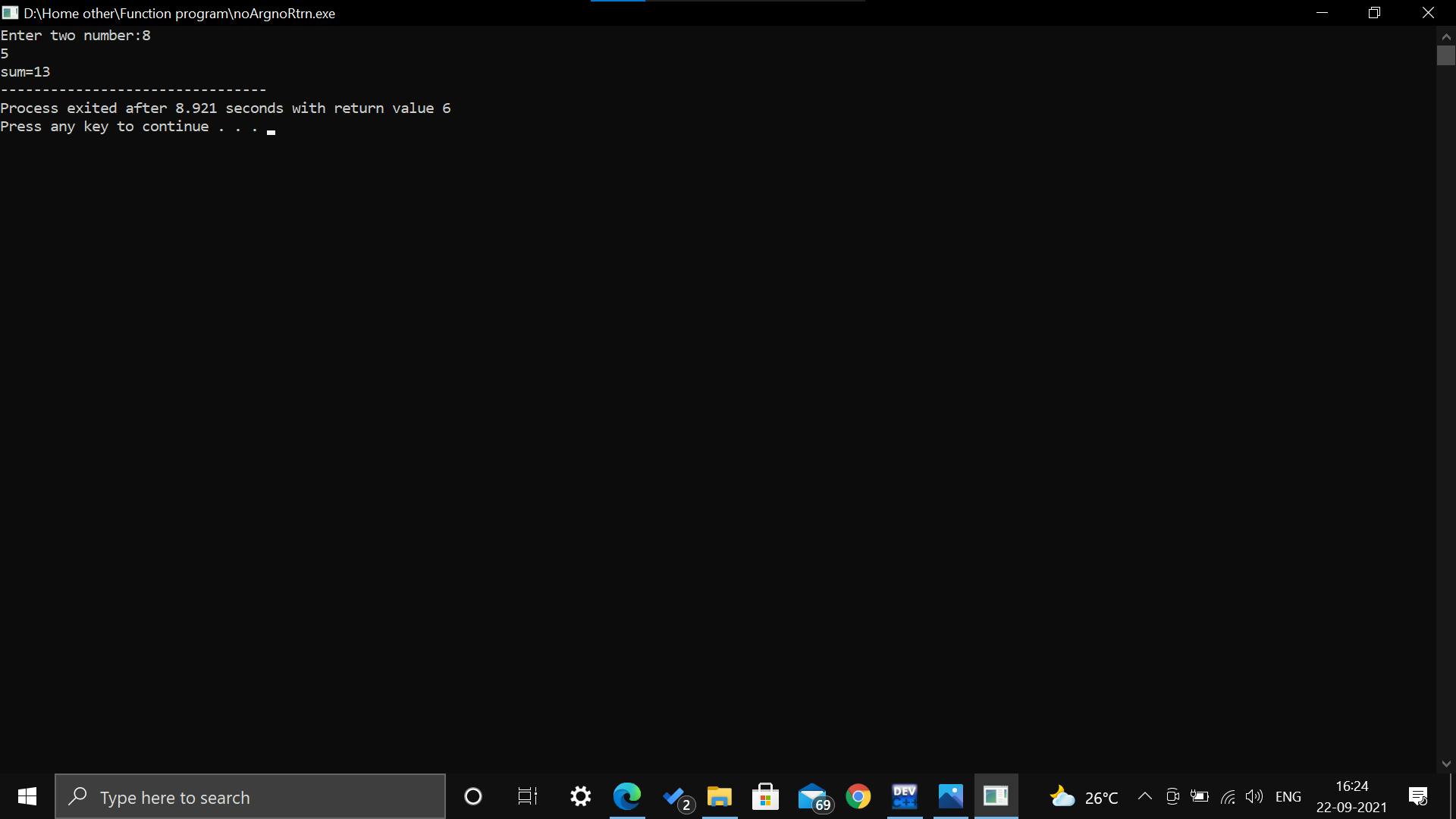
Output
Function without arguments and with return value: We can use the function without passing any arguments and the function will return any value in this aspect of function calls.
Output
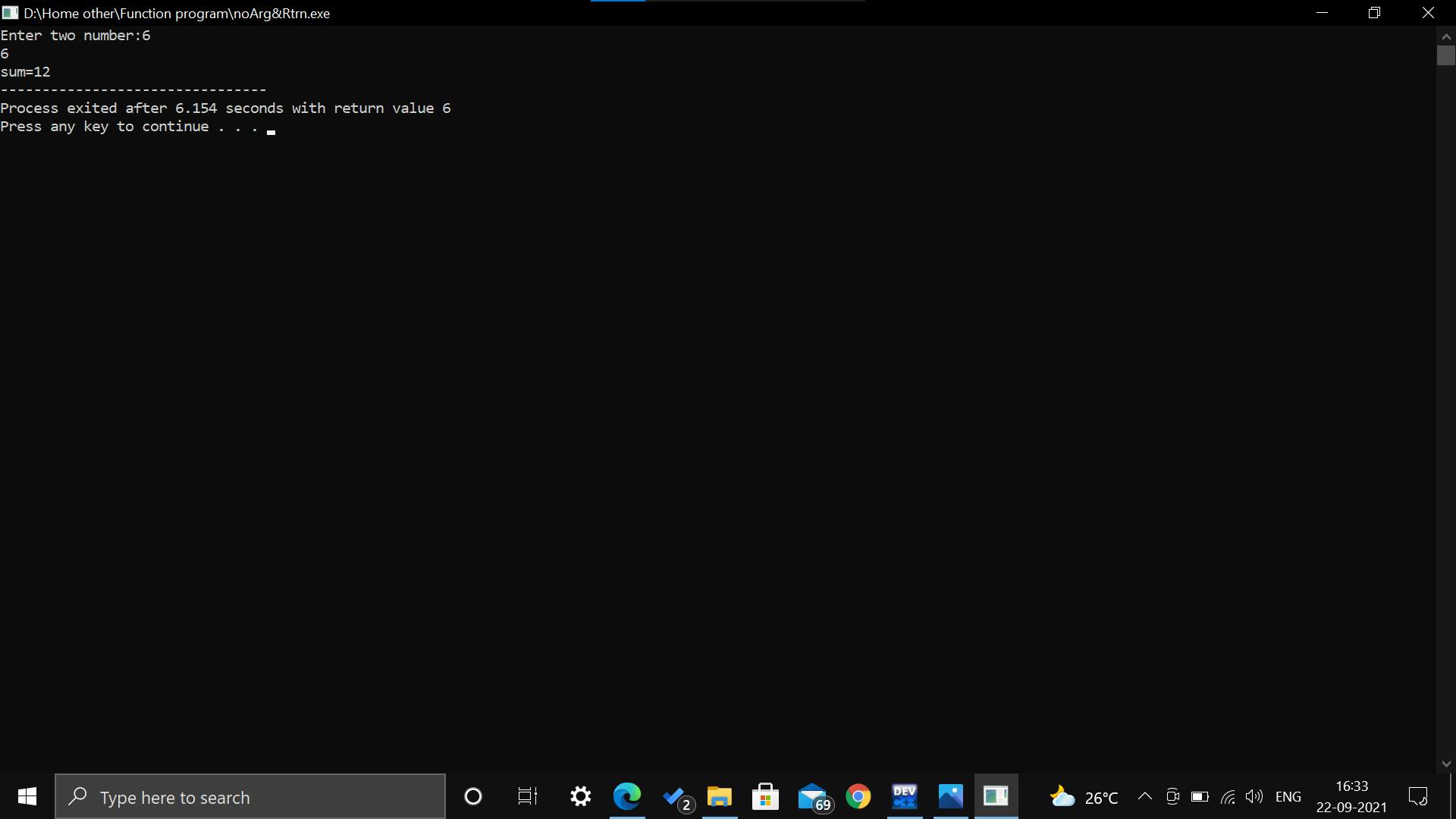
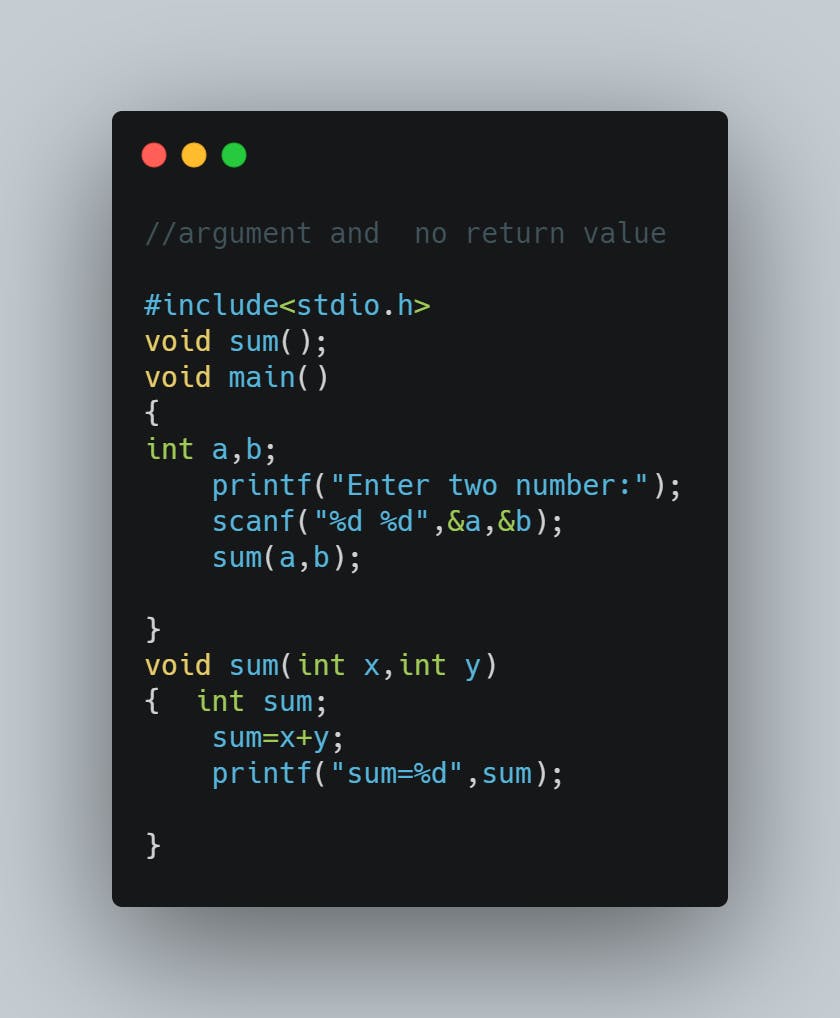
Function with arguments and without return value: We can use the function with passing any arguments and the function will not return any value in this aspect of function calls.
Output
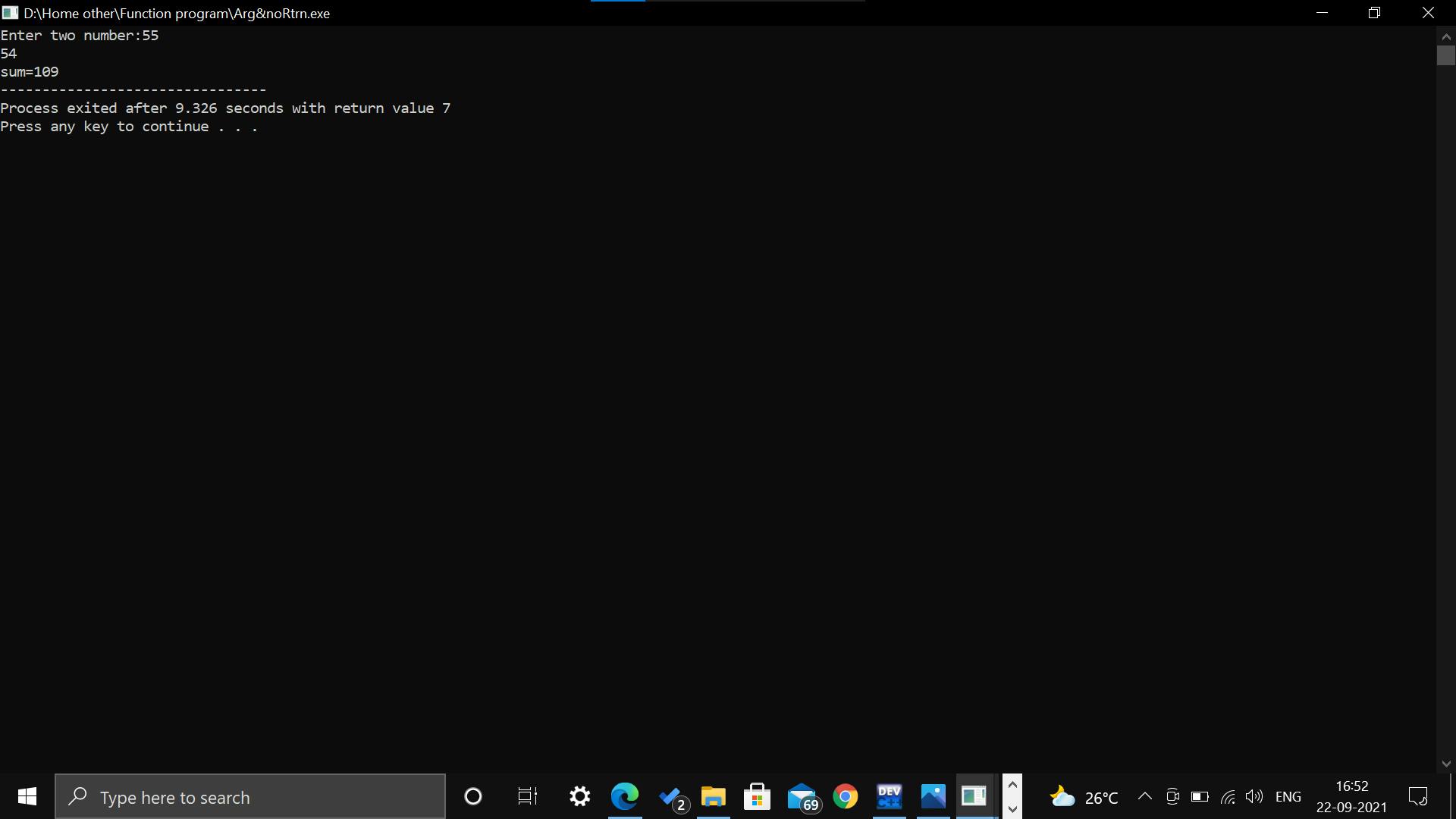
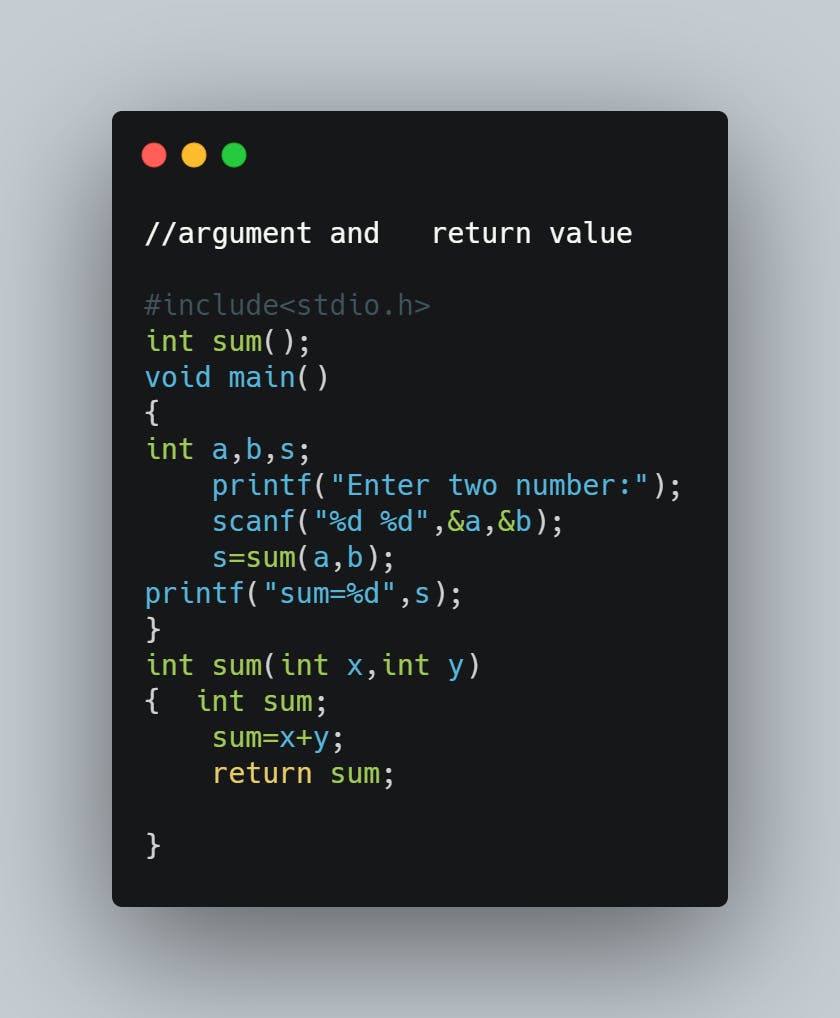
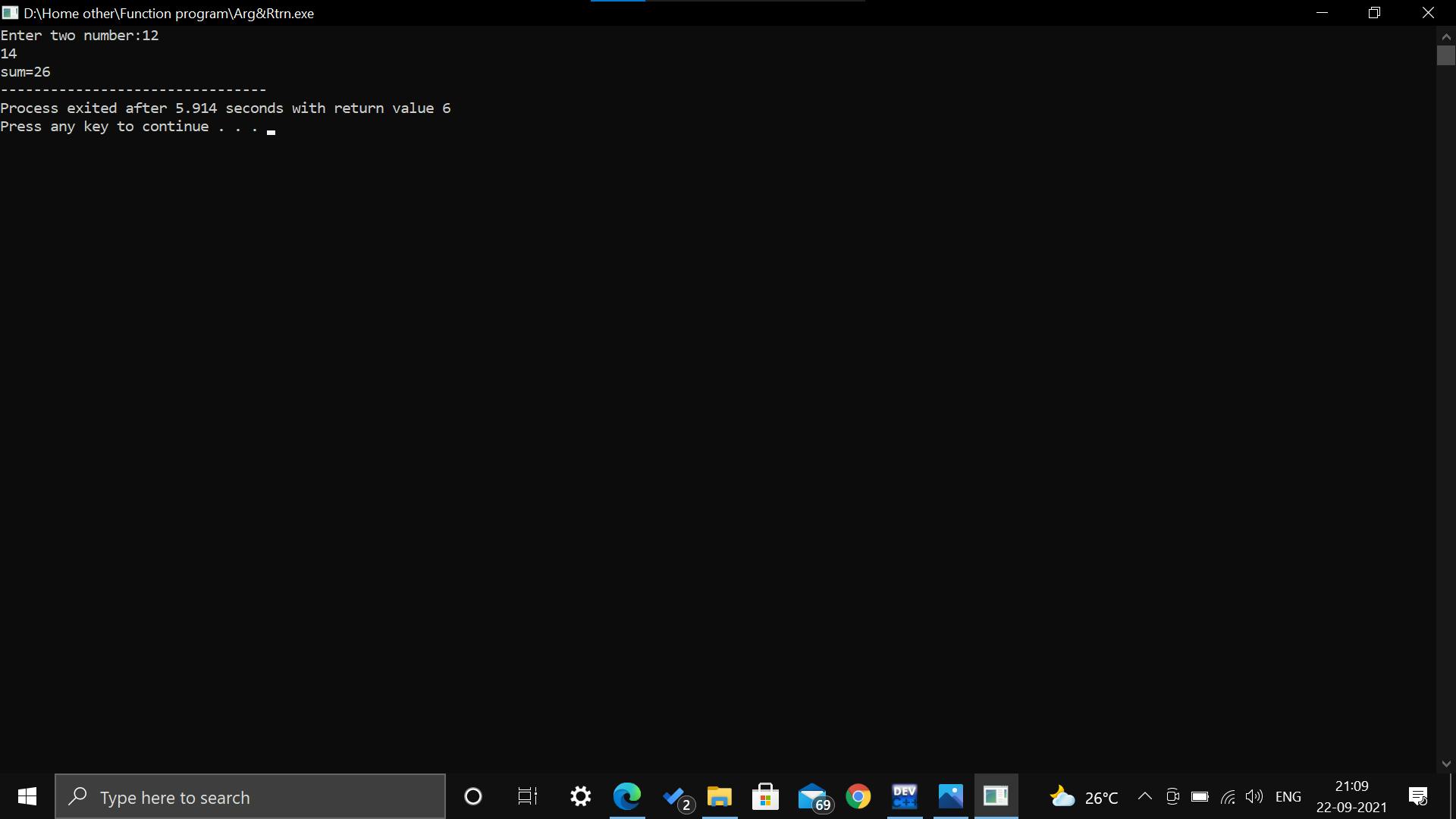
Function with arguments and return value: We can use the function with passing any arguments and the function will return any value to the compiler in this aspect of function calls.
Output
Function Arguments
If a function will use arguments, it must declare variables that accept the values of the arguments. These variables are called formal parameters. Formal parameters behave like local variables inside the function and are created upon entry into the function and destroyed upon exit. While calling a function, there are three ways in which arguments can be passed to a function.
Call by value
In call by value when we pass the formal value to the function, then it reflects the actual arguments.
Example

Call by reference
In call by reference, when we pass the formal value to the function, then it does not reflect the actual arguments.
Example

Call by address
In call by address, when we pass the address value to the function, then it does not reflect the actual arguments.
Example

Hope you have enjoyed the concepts of function in C in this post. Share your queries & doubts in the comment section, we will solve your doubts soon.
Thanks for reading.